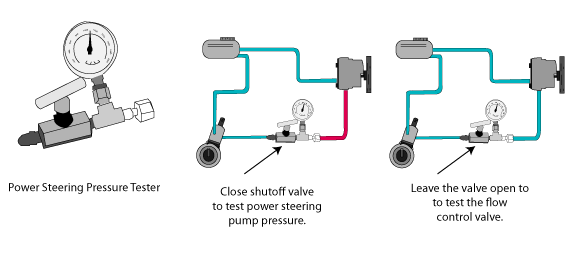
Power Steering Pressure Test
Personal safety
Whenever you perform a task in the workshop you must use personal protective clothing and equipment that is appropriate for the task and which conforms to your local safety regulations and policies. Among other items, this may include:
- Work clothing – such as coveralls and steel-capped footwear
- Eye protection – such as safety glasses and face masks
- Ear protection – such as earmuffs and earplugs
- Hand protection – such as rubber gloves and barrier cream
- Respiratory equipment – such as face masks and valved respirators
Safety check
- Be aware of moving drive belts and accessories when the engine is running.
- Power steering fluid can become very hot in operation. Take precautions to avoid burns.
- Power steering systems can reach a working pressure of over 1,000 pounds per square inch or 6,700Kpa during operation. Always follow manufacturers or equipment manufacturers procedure when working on the system.
- Power steering fluid is flammable. Always keep it away from hot exhaust manifolds, pipes, or catalytic converters.
- Clean up any spills immediately.
- Wear appropriate heat proof chemical gloves when the system is hot.
- Make sure that you understand and observe all legislative and personal safety procedures when carrying out the following tasks. If you are unsure of what these are, ask your supervisor.
Points to note
- Dispose of discarded fluid properly.
- Use only the specified power steering fluid for the vehicle.
- When the service is complete, check for le aks, check operation by turning the steering wheels to full lock in either direction and back to the center, and check the fluid level.
Points to note
A power steering pressure test checks the fluid pressure created by the power steering pump, control valve, and the pressure relief valve. Always get the manufacturers specifications and procedures before performing a power steering pump pressure test. Check the fluid levels, belt tension, external leaks, and make sure the tire pressures are correct.
A vehicle with low power steering pump pressure will require increased steering effort to steer. Sometimes the pressure may be erratic causing the wheel to jerk while turning the vehicle. Listen for any abnormal noises while turning the wheel. A squeal may be something as simple as a loose belt or weak belt tensioner.
- With the engine stopped install the pressure gauge with the shutoff valve in the open position.
- Start and idle the engine with the valve in the
- open position. Turn the wheel left and right several times to release any air bubbles and bring the fluid to normal operating temperature.
- With the gauge connected close the shutoff valve for 5 seconds and check against manufacturers specifications.
- Never hold this valve closed more than 5 seconds unless you are instructed to do so by the manufacturer of the pump.
- This will cause the fluid to overheat possibly damaging the power steering pump. If the reading is not within specifications the power steering pump must be replaced.
- With the shutoff valve in the open position check the gear housing for leaks by holding the wheel fully in one direction against its stop and checking fluid pressure against specifications. Do not hold the wheel in this position for too long. Power steering systems easily reach pressures in excess of 1000 lbs per square inch. If the pressure is too low the internal gear housing may have an internal leak undetectable during a visual inspection.
- Check the flow control valve operation with the shutoff valve in the open position and record the reading at 1000 RPM and 3000 RPM. Compare these two readings against specifications. If these two readings are not within specifications the flow control valve is bad and must be replaced.
 905 790 9339
905 790 9339